Knowledge Center
Nuclear Medicine
| 26 December 2025
Nuclear medicine has become one of the most trusted fields in modern healthcare due to its ability to diagnose and treat diseases at a very early stage. It combines advanced imaging, targeted therapies, and minimal side effects, making it a preferred choice for many conditions. As patients learn more about these procedures, they often discover how precise and reliable they truly are. Nuclear medicine continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for cancer care, thyroid disorders, and functional imaging, unlike anything before.
The uniqueness of nuclear medicine treatment lies in its ability to observe how the body functions from the inside rather than just looking at its physical structure. This makes it possible to detect diseases long before symptoms appear, allowing doctors to intervene early.
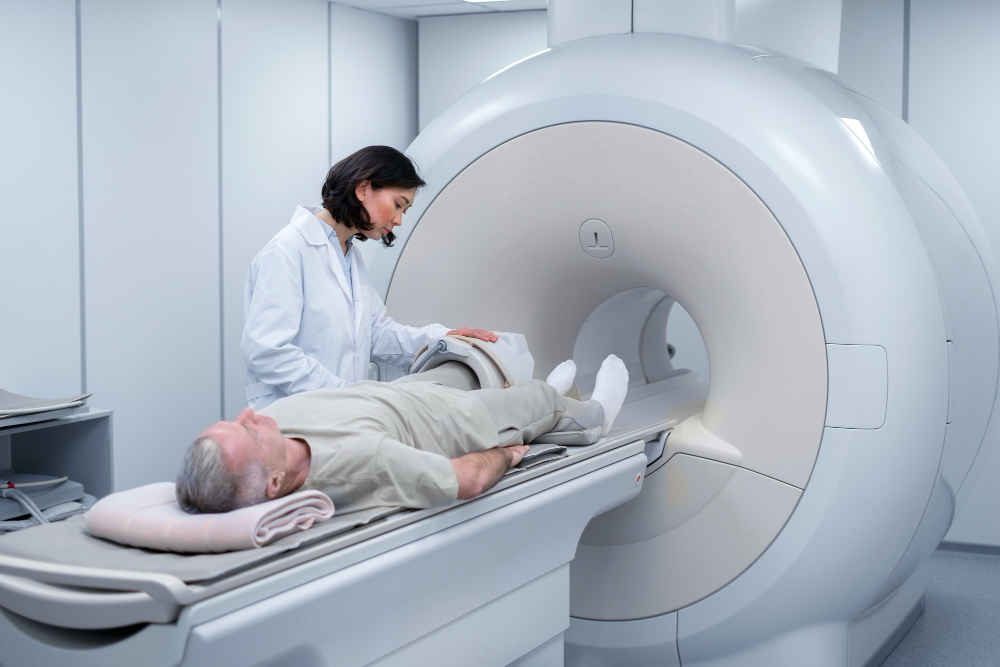
Modern imaging techniques like PET and SPECT have brought Nuclear medicine into a new era of accuracy and reliability. These machines create three-dimensional images that show how tissues absorb and process radioactive tracers. This level of detail helps doctors find abnormalities that may not appear in traditional X-rays or CT scans.
Radioactive materials used in healthcare are carefully regulated and scientifically proven to be safe when handled properly. The quantities administered during procedures are extremely small and designed to pass through the body naturally. They release controlled energy that is either captured by imaging machines or absorbed by diseased cells during treatment.
Brachytherapy has become one of the most effective internal radiation therapies, particularly for cancer patients. It offers a way to attack tumors from the inside while preserving surrounding healthy tissues. Many patients appreciate its fast treatment times and reduced side effects compared to external radiation. Because the radioactive source remains close to the cancer.
During Brachytherapy , doctors place a tiny radioactive source directly inside or very near a tumor. Once in place, the radiation acts locally, destroying cancer cells by damaging their DNA and preventing them from dividing. The placement of these sources is guided by imaging to ensure perfect accuracy. Because the radiation is concentrated in one area, healthy tissue around the tumor receives only minimal exposure.
There are two main forms of Brachytherapy : high-dose rate (HDR) and low-dose rate (LDR). HDR involves inserting a stronger radioactive source for short periods, often during outpatient visits, making it more convenient for many patients. LDR uses seeds that stay in the body longer, releasing radiation slowly over days or weeks to deliver a steady therapeutic effect.
Doctors typically recommend Brachytherapy when cancer is localized and confined to one area. It is commonly used for prostate, cervical, breast, and head and neck cancers, where tumors can be precisely targeted. Many patients receiving Brachytherapy benefit from faster recovery times and fewer complications compared to other treatments. Its targeted nature also makes it suitable for patients who cannot tolerate stronger systemic therapies.
Nuclear medicine offers diagnostic techniques that reveal how organs function, rather than just showing what they look like. This allows doctors to understand whether tissues are working as they should, providing early clues to disease. These diagnostic tools guide treatment decisions and help monitor progress over time. Patients often find these scans more informative than conventional imaging because they offer functional insights that shape more accurate diagnoses.
Functional imaging detects diseases by observing how the body processes energy, nutrients, and blood flow. For example, a heart scan may reveal poor circulation long before a patient feels chest pain. The ability to identify such abnormalities early makes functional imaging an invaluable tool for disease prevention and treatment planning.
Nuclear scans provide detailed information about disease behavior inside the body, allowing doctors to customize treatment plans. They help determine the most effective therapy by showing how aggressively a disease is progressing. When specialists can see whether a tumor is responding to treatment, they can adjust the dosage or strategy immediately.
Most Nuclear medicine scans are straightforward, comfortable, and painless. Patients simply lie still while the scanner takes images, with the entire process usually lasting less than an hour. The amount of radiation exposure is minimal, comparable to what the body receives naturally over time. After the scan, patients can return to normal activities without restrictions.
radioactive iodine therapy, commonly known as I-131 therapy, plays a major role in treating thyroid disorders, especially thyroid cancer and hyperthyroidism. This therapy works because the thyroid naturally absorbs iodine, making it a perfect target for treatment. Patients often find this therapy convenient, non-invasive, and highly effective compared to more aggressive treatment options.
radioactive iodine therapyis specifically used for thyroid disorders because thyroid cells absorb iodine more efficiently than any other cells in the body. When patients swallow radioactive iodine, it travels directly to the thyroid, where it accumulates and begins to shrink overactive or cancerous tissue. This targeted approach reduces symptoms quickly and prevents further growth of abnormal cells.
Radioactive iodine targets cancer cells by delivering radiation directly to the thyroid without affecting surrounding organs. It is absorbed by both normal and abnormal thyroid cells, but cancer cells tend to retain the radioactive iodine longer, resulting in more effective treatment. The radiation disrupts the cell’s ability to divide, gradually destroying cancerous tissue.
Before undergoing radioactive iodine therapy, patients may need to follow a low-iodine diet to increase the thyroid’s absorption of the radioactive dose. Once the treatment begins, the process is as easy as swallowing a capsule and waiting for the iodine to work internally. Mild side effects such as dry mouth, neck tenderness, or fatigue may occur but usually resolve quickly.
Nuclear medicine procedures offer an impressive range of benefits that improve both diagnosis and treatment quality. Their ability to detect diseases early, target treatments precisely, and minimize side effects places them at the forefront of modern healthcare. Patients benefit from quicker recoveries, fewer complications, and highly personalized treatment plans.
A major benefit of treatments like Brachytherapy and radioactive iodine is their precise targeting ability. They deliver therapeutic radiation directly to the affected area while sparing healthy tissues. This reduces the risk of long-term side effects and preserves vital organs. Because radiation does not spread throughout the body, patients experience fewer complications compared to traditional therapies. Precision targeting also increases the effectiveness of treatment, as high doses can be safely delivered to cancer cells without harming surrounding structures.
Nuclear imaging allows doctors to detect diseases when they are still in their earliest stages, often before any noticeable symptoms appear. This early detection gives patients more time to start treatment and increases the chances of a positive outcome. For conditions like cancer and heart disease, early diagnosis can make a dramatic difference in survival rates.
Personalized treatment is one of the major strengths of nuclear medicine. Doctors create customized plans based on how a patient's body responds during scans and treatment sessions. When physicians can observe disease progression or treatment impact in real time, they can adjust therapy instantly. This results in better outcomes and fewer complications.
Although Nuclear medicine procedures are generally safe, it is important for patients to understand possible risks. Radiation exposure is kept extremely low, but some short-term or long-term effects can still occur. With proper planning and medical guidance, these risks can be minimized. Most patients tolerate nuclear medicine treatments well and return to daily activities quickly.
Radiation exposure during Nuclear medicine procedures is much lower than most people expect. The doses used are carefully calculated to ensure safety while still providing effective results. Patients are exposed to amounts comparable to what they naturally encounter in the environment over several months. Doctors consider factors such as age, health history, and previous exposures before recommending treatment.
Some patients may experience short-term side effects such as mild fatigue, nausea, or discomfort around the treatment area. These effects are usually temporary and disappear within a few days without requiring additional treatment. During this time, rest and hydration can help speed up recovery. The side effects occur as the body processes the radioactive material, which gradually loses its activity.
Long-term side effects from nuclear medicine are rare but may include mild tissue changes depending on the treated area. Doctors monitor patients through follow-up visits to ensure that all internal functions remain normal. Over time, the body recovers fully from radiation exposure, and most patients do not experience lasting issues.
Patients often compare different Nuclear medicine procedures to understand which one suits their condition best. Each method has unique strengths and specific uses. By learning how they differ, patients can make clearer and more confident healthcare decisions. Doctors help guide this process by explaining how each option works and what to expect. Understanding the differences ensures that treatment is both effective and aligned with personal health needs.
When comparing Brachytherapy with external radiation, the main difference lies in how radiation is delivered. External radiation is treated from outside the body and covers a larger area, while Brachytherapy focuses radiation directly within the tumor. This internal placement allows for higher doses of radiation without harming surrounding tissues. Brachytherapy generally offers shorter treatment times and fewer side effects.
Nuclear imaging differs from conventional scans because it examines how organs function rather than just their physical appearance. Conventional scans like X-rays focus on structures, while nuclear scans evaluate activities such as blood flow or metabolism. This functional insight helps detect disease much earlier. Nuclear imaging also offers clarity in cases where traditional scans show no visible abnormalities.
PET Scans Explained: How They Help Diagnose Diseases
Radioactive iodine offers a unique advantage compared to other thyroid treatments because it targets thyroid tissue exclusively. Other treatments, such as medications or surgery, may affect more areas of the body or require longer recovery periods. Radioactive iodine works internally and often resolves thyroid problems with just one session. It is especially effective for hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer.
Nuclear medicine continues to revolutionize the way diseases are diagnosed and treated by offering safe, precise, and highly effective solutions. From targeted therapies like brachytherapy to advanced imaging techniques and radioactive iodine therapy, its benefits extend far beyond traditional medical approaches. While there are risks involved, they remain minimal when compared to the life-changing advantages these procedures offer. As technology advances, nuclear medicine will continue to play a vital role in ensuring better health outcomes for millions of people worldwide.
Nuclear medicine procedures use low and carefully controlled levels of radiation, making them safe for most patients when performed under medical supervision.
Yes, nuclear imaging can identify functional abnormalities early, often before physical symptoms develop.
It usually leaves the body within hours or days through natural processes such as urine or sweat.